CSAPP-6-cachelab
1.cachelab 引言
参考:
- csapp-cachelab 详解 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
- csapp实验5-cachelab实验详解-CSDN博客
- CSAPP(CMU 15-213):Lab4 Cachelab详解-CSDN博客
非常感谢!!!
描述:part a 是实现cache的模拟器,part b 将针对缓存性能进行优化,写一个矩阵转置函数
2. Part A
规则:
- 模拟器必须对任意的s,E和b正确工作,意味着必须使用
malloc函数作为函数模拟器的数据结构体分配空间 - 本实验只对数据缓存性能感兴趣,因此应该忽略所有指令缓存访问,valgrind 总是将 i 放在第一位,将
M(modify) L(load) S(store)放在第二列。 - 为了获得分数,必须在主函数末尾调用
printSummary(hit_count, miss_count, eviction_count); - 对于本实验,应该假设内存访问已经正确对齐,因此单个内存访问永远不会越界。
思路:
缓存结构:

- cache地址中包含标记tag,组索引s和块偏移b
- 首先会根据组索引在cache中找到组
- 然后如果该组中是有效的,并且标记tag能够匹配上 那么就hit
- 如果没有匹配hit,那么就是miss,把需要的块替换进来
- 组没有满的情况下直接替换即可,组满了的情况下需要根据
LRU进行替换
由规则可以知道只需要在
csim.c文件中实现对S L M这三种类型的地址操作然后反映出相应的结果miss(未命中) hit(命中) eviction(驱逐)。并且采用LRU(least-recently used)策略,既是发生eviction时 选择最近最少访问的那一行。查看官方文档6.1建议用
getopt实现对命令行的读取和解析1
2
3
4//头文件
需要实现的
创建结构体: 模拟缓存中的数据结构,参考上图缓存结构,每一行有效位,标记位和缓存块,因为需要使用导LRU 所以还需要记录每一行的时间戳:
1
2
3
4
5
6typedef struct cacheLine{
int isValid; //有效位
//bool isValid; //c 没有原生的bool
int tag; //标记位和数据位
int LRU_time; //时间戳
}cacheLine;常见整个cache的结构体,包含每一个组,组内每个行,行中数据位字节数,以及每一个块的数据结构
cacheLine:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8//定义整个cache
typedef struct cache
{
int nSets; //组
int nLines; //每组块数 行数
int bblocks; //每块字节数
cacheLine** block;
}cache;对cache进行初始化 包括申请每个组 组内每一行的空间,以及对每一行进行初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23//初始化cache s组,E行,b字节的cache,并且设置每一行的有效位,标记位和时间戳
void initCache(int s, int E, int b) {
int S = 1 << s; // 2^s 组
int B = 1 << b; // 2^b个字节数据
Cache* myCache= (Cache *)malloc(sizeof(Cache));
myCache->nSets = S;
myCache->nLines = E;
myCache->bblocks = B;
//每组进行空间开辟 申请空间
myCache->block = (CacheLine**)malloc(sizeof(CacheLine *) * S);
for (size_t i = 0; i < S; i++) {
//每行进行空间开辟
myCache->block[i] = (CacheLine*)malloc(sizeof(CacheLine) * E);
for (size_t j = 0; j < E; j++)
{
//每行进行初始化
myCache->block[i][j].isValid = 0; //有效位设置0
myCache->block[i][j].tag = -1; //标志位-1
myCache->block[i][j].LRU_time = 0; //时间戳0
}
}
}判断是否命中模块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11//判断是否命中 命中则返回块的索引
int isHit(int opSet, int opTag, Cache* myCache) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < myCache->nSets; i++)
{
//只有当该行的有效值存在且 标志位能够匹配时才返回
if (myCache->block[opSet][i].isValid && myCache->block[opSet][i].tag == opTag) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}如果没Hit,那么就是要判断当前cache是否是全满了,如果没有全满则返回任意一个有效位为0的行作为替换行,满了则返回会-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9//miss了 判断是否满了,没有满则选择一个有效位为0的进行替换返回该索引
int isFull(int opSet, Cache* myCache) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < myCache->nLines; i++) {
if (myCache->block[opSet][i].isValid == 0) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}如果没有满,则直接替换返回的标号,然后更新LRU。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12//如果没有满则将行进行替换,并且更新LRU LRU越大表示越久没有访问过
void cacheReplace(int i, int opSet, int opTag, Cache* myCache) {
myCache->block[opSet][i].isValid = 1;//合法
myCache->block[opSet][i].tag = opTag;//标记位
//更新时间戳
for (size_t j = 0; i < myCache->nLines; j++) {
//如果有效
if (myCache->block[opSet][j].isValid == 1) {
myCache->block[opSet][j].LRU_time++;//加一
}
}
}找到最大的LRU的索引并返回
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13//如果满了则找最大的LRU进行替换,查找有效位为1且时间戳最大的时间戳返回
int findMaxLRU(int opSet, Cache* myCache) {
int maxTempLRU = 0;
int maxIndexLRU = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < myCache->nLines; i++)
{
if (myCache->block[opSet][i].LRU_time > maxTempLRU) {
maxTempLRU = myCache->block[opSet][i].LRU_time;
maxIndexLRU = i;
}
}
return maxIndexLRU;
}整合逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29//整合更新策略
void cacheUpdate (int opSet, int opTag, Cache* myCache) {
//判断
if (isHit(opSet, opTag, myCache) == -1) {
//如果没有命中 则需要进行替换
missCount++;
if (verbose) {
printf("miss"); //跟踪信息打印
}
//判断是否满了
int index = isFull(opSet, myCache);
if (index == -1) {
evictionCount++; //驱除+1
if (verbose) {
printf("eviction \n"); //跟踪信息打印
}
index = findMaxLRU(opSet, myCache); //找到最大LRU的索引
}
cacheReplace(index, opSet, opTag, myCache);//单行替换
} else {
//hit
hitCount++;
if (verbose) {
printf("hit \n");
}
cacheReplace(isHit(opSet, opTag, myCache), opSet, opTag, myCache);
}
}释放malloc开辟的内存
1
2
3
4
5//free 用malloc申请了内存
void freeCache() {
free(myCache);
myCache = NULL;
}对输入的文件进行解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32void getTrace(int s, int E, int b) {
FILE *p_file;
p_file = fopen(t, "r");
if (p_file == NULL) {
exit(-1);
}
char identifier;
unsigned address; //无符号数表示地址
int size;
while (fscanf(p_file, " %c %x,%d", &identifier, &address, &size) > 0) {
//取出相应的位
int opTag = address >> (s + b);
int opSet = (address >> b) & ((unsigned)(-1) >> (8 * sizeof(unsigned) - s));
switch (identifier)
{
case 'M':
cacheUpdate(opSet, opTag);
cacheUpdate(opSet, opTag);
break;
case 'L':
cacheUpdate(opSet, opTag);
break;
case 'S':
cacheUpdate(opSet, opTag);
break;
}
}
fclose(p_file);
}usage函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13void usage() {
printf("Usage: ./csim-ref [-hv] -s <num> -E <num> -b <num> -t <file>\n");
printf("Options:\n");
printf(" -h Print this help message.\n");
printf(" -v Optional verbose flag.\n");
printf(" -s <num> Number of set index bits.\n");
printf(" -E <num> Number of lines per set.\n");
printf(" -b <num> Number of block offset bits.\n");
printf(" -t <file> Trace file.\n\n");
printf("Examples:\n");
printf(" linux> ./csim-ref -s 4 -E 1 -b 4 -t traces/yi.trace\n");
printf(" linux> ./csim-ref -v -s 8 -E 2 -b 4 -t traces/yi.trace\n");
}主函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55//定义返回参数
Cache *myCache = NULL;
int missCount = 0;
int hitCount = 0;
int evictionCount = 0;
int verbose = 0; //跟踪信息标志
char t[50];
extern char *optarg;
int main(int argc, char **argv){
//读取命令行参数
char opt;
int s, E, b;
int wrongArg = 0;
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "hvs:E:b:t:")) != -1) {
switch (opt)
{
case 'h':
wrongArg = 1;
break;
case 'v':
verbose = 1; //跟踪信息可选标志
break;
case 's':
s = atoi(optarg);//ascii to int
break;
case 'E':
E = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'b':
b = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 't':
strcpy(t, optarg);
break;
default:
usage();
break;
}
}
if (s <= 0 || E <= 0 || b <= 0 || wrongArg == 1) {
usage();
return 0;
}
//声明
initCache(s, E, b);
getTrace(s, E, b);
freeCache();
printSummary(hitCount, missCount, evictionCount);
return 0;
}
结果:

3.Part B
在trans.c中编写函数,尽可能的少的缓存未命中行为。
建议
- 每个转置函数最多可以使用12个int类型的局部变量
- 不可以使用任何long类型或者技巧来规避上一条
- 不可以使用递归
- 堆栈上局部局部变量不允许超过12个
- 转置函数不可能修改数组a,但是可以对数组b的内容执行任何想要的操作
- 不允许在代码中使用任何数组或者使用malloc的变体
思路:
- 充分利用cache的能力,尽量不访问内存,提高矩阵的时间局部性和空间局部性
- 采取直接映射
E = 1,需要重点注意矩阵对角线上的情况,因为如果数组A的起始地址为0x30a080,那数组B 的起始地址位0x34a080,两个数组在对角线上的元素会被映射同一块 - 给出信息
s = 5,E = 1, b = 5,即缓存有2^5 = 32个组, 采取直接映射(cache line),每一块(block)数据位存储了2^5 = 32个字节也就是8个int(一个int 占据4 字节)。 所以总共有1KB的直接映射高速缓存
M = 32 , N = 32
- 数组A是以行来访问的,数组B是以列来访问,那么对于一个cache 可以存储数组的前8行所有的元素,而在访问数组B第九行的第一个元素之后,会将之前存储的八行的cache全部冲突替换,导致没有重复利用cache数据,只利用了每个块的一个元素
- 故为了提高cache,在cache载入后将cache包含的全部元素操作后在替换cache,保证不会二次载入相同的cache,设置子块的大小为8x8
- 分块操作
模拟一下缓存的进行转置的过程
首先明确的是 数组在内存中是按照行存放的,多维数组也是如此,相邻的两行前一行的尾元素与下一行的首元素地址相连。(假设4X4矩阵 那么a03和a10地址相连)
Part B中的cache结构如下:

这么看可能不是很好理解 如果按照数组排列 即一行存放32个数组元素可以得出下图:即每一行

模拟:
- 假设
A[0][0]set为 00 ,那么一开始需要从内存中载入 会造成一次miss,然后令temp = A[0][0],B[0][0] = temp,写入B的时候会先Load 一次,此时B[0][0]的 set 也为00,会造成第一行的驱逐 - 加载
A[0][1]-A[0][7]的时候,又会从内存中加载A数组,此时B[1-7][0] = A[0][1-7]而此时B[1][0]的SET 与A[0][1]不会再相等,故只有加载时候的miss ,没有eviction - 然后继续反复。
- 到
A[0][8-15]和B[8-15][0]的时候此时B[0-7][0]对应的SET相等,然后每次搬运的过程中 会出现大量的eviction
分块的方法解决思路:
- 将
32 X 32分割为8 X 8如下:(参考见水印) 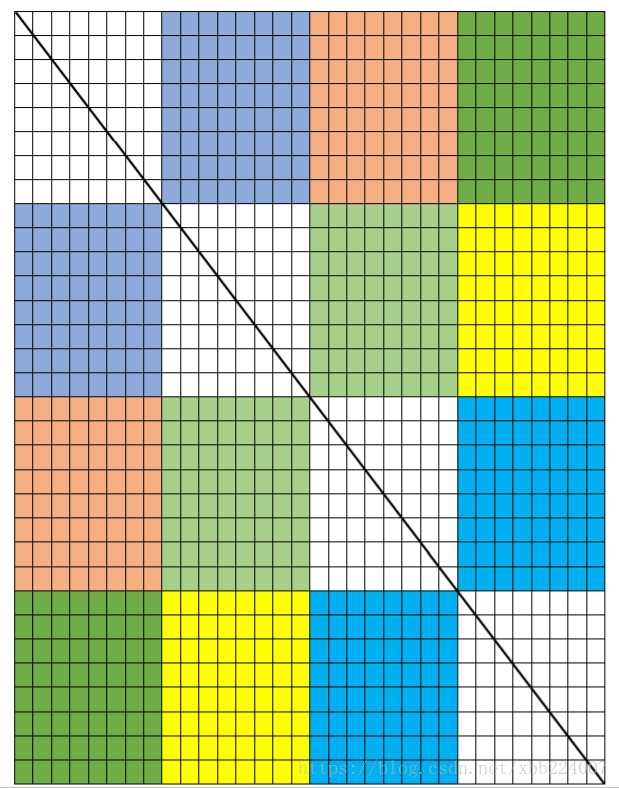
- 因为当
SET = 0的时候A[0][0-7]当SET = 1此时存放的是原数组的A[1][0-7]而不是 上面所说的A[0][8-15]. A[1][0-7]转置为B[0-7][1]不会对cache造成eviction而是补充在B[0-7][0]后面。
分块代码:
1 | for (int m = 0; m < 32; m += 8){ //分块逻辑 块遍历 |
- 上述代码在对角线两侧的区域已经优化的足够好了 但是对于对角线上的元素来说,每次进行转置都会映射到相同的区域会造成miss 和 eviction
- 解决方案:将A中的元素一行行的不转置防止在B中,然后对B矩阵中原地址进行转置 这样就不会造成不必要的eviction只存在替换时候的miss
优化代码:
1 | int _0, _1, _2, _3, _4, _5, _6, _7; |
结果:

M = 64 , N = 64
- 如同
32 x 32一样可以将矩阵划分成4 X 4的子块,但是这样会导致cache没有利用完全,同样也会miss很多 - 如果使用
8 X 4则每一个cache只有四个 int 数据会被利用到 - 可以把部分数据放入到数组B的cache中,避免局部变量数目的限制
- 以下参考: CSAPP(CMU 15-213):Lab4 Cachelab详解-CSDN博客


代码实现:
1 | void transpose_submitB(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N]) { |
M = 61, N = 67
无法进行对齐,可以采用变化分块进行处理
代码实现:
1 | void transpose_submitC(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N]) { |
结果:

