9.物理内存管理的实现
9.1分页式的内存管理

线性地址是连续的,但是其实际指向的 物理地址就不见得是连续的了
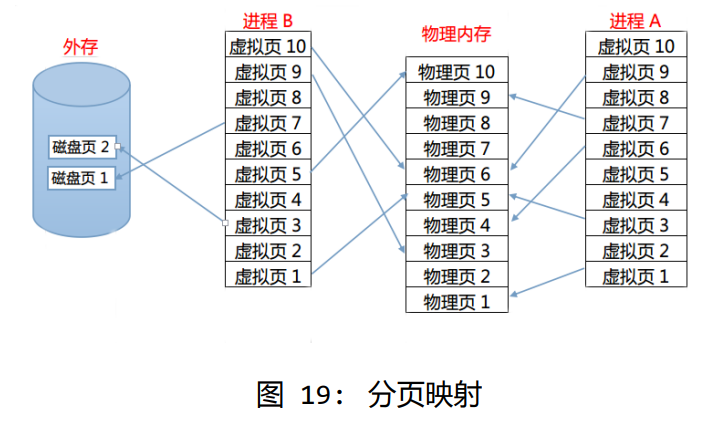
虚拟 内存实质上就是把物理内存中暂时用不到的内容暂时换出到外存里,空出内存放置现阶段 需要的数据。至于替换的策略当然有相应的算法了,比如最先换入原则,最少使用原则等 等方法可以使用
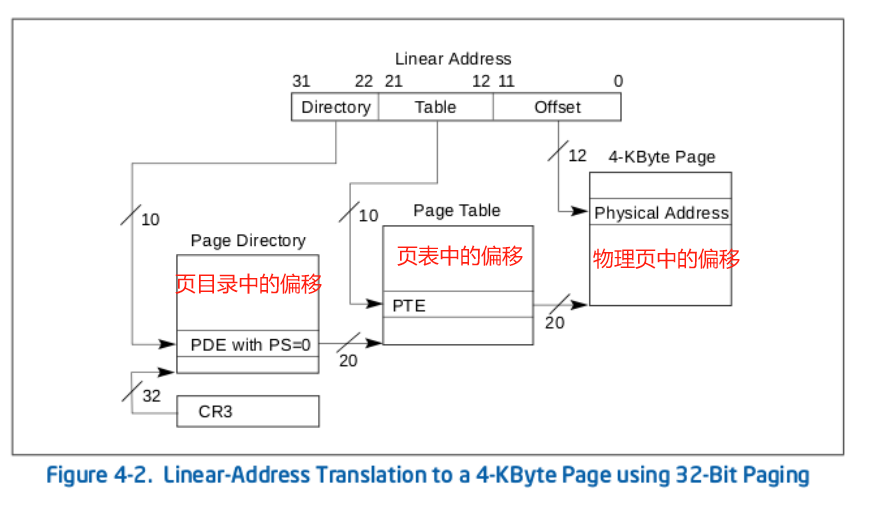
分级页表:以32位的地址来说,分为3段来寻址,分别是地址的低12位,中间10位和高10位。
- 高 10位表示当前地址项在页目录中的偏移,最终偏移处指向对应的页表,
- 中间10位是当前地 址在该页表中的偏移,我们按照这个偏移就能查出来最终指向的物理页了,
- 最低的12位表 示当前地址在该物理页中的偏移
本章主要解决一下三个问题:
- 如何获取可用物理内存的大小和地址?
- 采用什么样的数据结构来描述物理内存?
- 申请和释放物理内存的算法如何实现?
问题一:如何获取可用物理内存的大小和地址?
在GRUB中已经获取物理内存的分布,并且将它们放置下面的成员里
include/multiboot.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| 1 typedef
2 struct multiboot_t {
3
4 ... ...
5
6
11 uint32_t mmap_length;
12 uint32_t mmap_addr;
13
14 ... ...
15
16 } __attribute__((packed)) multiboot_t;
17
18
24 typedef
25 struct mmap_entry_t {
26 uint32_t size;
27 uint32_t base_addr_low;
28 uint32_t base_addr_high;
29 uint32_t length_low;
30 uint32_t length_high;
31 uint32_t type;
32 } __attribute__((packed)) mmap_entry_t;
|
GRUB将内存探测的结果按每个分段整理为mmap_entry结构体的数组。mmap_addr是这 个结构体数组的首地址,mmap_length是整个数组的长度。
mm/pmm.c 打印所有物理内存段的操作:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| #include "multiboot.h"
#include "common.h"
#include "debug.h"
#include "pmm.h"
void show_memory_map(){
uint32_t mmap_addr = glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_addr;
uint32_t mmap_length = glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_length;
printk("Memory map:\n");
mmap_entry_t *mmap = (mmap_entry_t *)mmap_addr;
for (mmap = (mmap_entry_t *)mmap_addr; (uint32_t)mmap < mmap_addr + mmap_length; mmap++) {
printk("base_addr = 0x%X%08X, length = 0x%X%08X, type = 0x%X\n",
(uint32_t)mmap->base_addr_high , (uint32_t)mmap->base_addr_low ,
(uint32_t)mmap->length_high , (uint32_t)mmap->length_low ,
(uint32_t)mmap->type);
}
}
|
script/kernel.ld
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| PROVIDE( kern_start = . ); // 加上这两个变量
.text :
{
*(.text)
. = ALIGN(4096);
}
.data :
{
*(.data)
*(.rodata)
. = ALIGN(4096);
}
.bss :
{
*(.bss)
. = ALIGN(4096);
}
.stab :
{
*(.stab)
. = ALIGN(4096);
}
.stabstr :
{
*(.stabstr)
. = ALIGN(4096);
}
PROVIDE( kern_end = . ); // 加上这两个变量
|
需要知道内核本身加载到物理内存的信息,通过链接器脚本
添加头文件 include/pmm.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| #ifndef INCLUDE_PMM_H
#define INCLUDE_PMM_H
#include "multiboot.h"
extern uint8_t kern_start[];
extern uint8_t kern_end[];
void show_memory_map();
#endif
|
修改入口代码 init/entry.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| #include "types.h"
#include "console.h"
#include "debug.h"
#include "gdt.h"
#include "idt.h"
#include "timer.h"
#include "pmm.h"
int kern_entry(){
init_debug();
init_gdt();
init_idt();
console_clear();
printk_color(rc_black, rc_green, "Hello OS!!!\n");
init_timer(200);
printk("kernel in memory start: 0x%08X\n", kern_start);
printk("kernel in memory end: 0x%08X\n", kern_end);
printk("kernel in memory used: %d KB\n\n", (kern_end - kern_start + 1023) / 1024);
show_memory_map();
return 0;
}
|
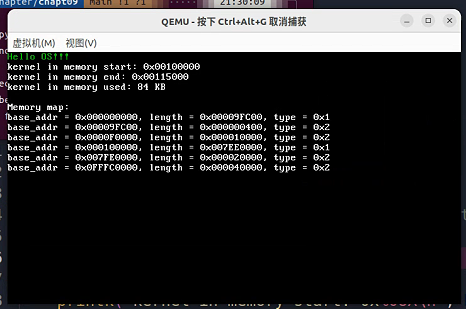
可用内存是两段 type1 表示ram可用内存,是1MB以下的0x0-0x9FC00和1M以上的0x100000-0x7EFE000两段。
本身的内核程序起始位置是 0x100000(1MB) 占用的内存大小为84KB
问题二:采用什么样的数据结构来描述物理内存?
物理内存管理法— 伙伴算法:伙伴算法在申请和释放物理页框的时候会对物理页框进行合并操作,尽可能的 保证可用物理内存的连续性。
- 内部碎片:内部碎片就是已经被分配出去却不能被利用的内存空间,比如我们为了管理 方便,按照4KB内存块进行管理
- 外部碎片:内存频繁请求和释放大小不同的连续页框后,导致在已分配页框块周围分散了许多小 块空闲的页框,尽管这些空闲页框的总数可以满足接下来的请求,但却无法满足一个大块 的连续页框。
本项目涉及的内存管理方法:将物理页面的管理地址设定在1MB以上内核加载的结束位置之后,从这个起始位置到512MB的地址处将所有的物理内存按页划分, 将每页的地址放入栈里存储。这样在需要的时候就可以按页获取到物理内存了 — 通过栈实现
主要的步骤:
- (kern_end - kern_start)内核加载完的结束位置到512MB的位置按照一个页4KB的大小划分页框
- 将页框依次压入栈中 — 每个页框的地址都会被记录下来
- 当需要分配使用物理内存的时候,弹出相应大小的页框地址
- 当系统释放内存的时候,将页框重新压入栈中
示例:
假设内核加载结束位置是2MB(0x200000),那么从2MB到512MB的范围内的所有内存按4KB页框划分。栈中存储的地址可能依次是:
1
| 0x00200000, 0x00201000, 0x00202000, ..., 0x1FFFE000
|
当需要分配一个页框时,从栈中弹出一个地址,如0x00200000,然后将这个页框分配给需要的任务。当任务完成并释放这个页框时,地址0x00200000重新压入栈中,等待下次分配。
include/pmm.h 头文件修改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| #ifndef INCLUDE_PMM_H
#define INCLUDE_PMM_H
#include "multiboot.h"
#define STACK_SIZE 8192
#define PMM_MAX_SIZE 0x20000000
#define PMM_PAGE_SIZE 0x1000
#define PAGE_MAX_SIZE (PMM_MAX_SIZE / PMM_PAGE_SIZE)
#define PHY_PAGE_MASK 0xFFFFF000
extern uint8_t kern_start[];
extern uint8_t kern_end[];
extern uint32_t phy_page_count;
void show_memory_map();
void init_pmm();
uint32_t pmm_alloc_page();
void pmm_free_page(uint32_t p);
#endif
|
mm/pmm.c 文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| #include "multiboot.h"
#include "common.h"
#include "debug.h"
#include "pmm.h"
static uint32_t pmm_stack[PAGE_MAX_SIZE+1];
static uint32_t pmm_stack_top;
uint32_t phy_page_count;
void show_memory_map(){
uint32_t mmap_addr = glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_addr;
uint32_t mmap_length = glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_length;
printk("Memory map:\n");
mmap_entry_t *mmap = (mmap_entry_t *)mmap_addr;
for (mmap = (mmap_entry_t *)mmap_addr; (uint32_t)mmap < mmap_addr + mmap_length; mmap++) {
printk("base_addr = 0x%X%08X, length = 0x%X%08X, type = 0x%X\n",
(uint32_t)mmap->base_addr_high , (uint32_t)mmap->base_addr_low ,
(uint32_t)mmap->length_high , (uint32_t)mmap->length_low ,
(uint32_t)mmap->type);
}
}
void init_pmm()
{
mmap_entry_t *mmap_start_addr = (mmap_entry_t *)glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_addr;
mmap_entry_t *mmap_end_addr = (mmap_entry_t *)glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_addr + glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_length;
mmap_entry_t *map_entry;
for (map_entry = mmap_start_addr; map_entry < mmap_end_addr; map_entry++) {
if (map_entry->type == 1 && map_entry->base_addr_low == 0x100000) {
uint32_t page_addr = map_entry->base_addr_low + (uint32_t)(kern_end - kern_start);
uint32_t length = map_entry->base_addr_low + map_entry->length_low;
while (page_addr < length && page_addr <= PMM_MAX_SIZE) {
pmm_free_page(page_addr);
page_addr += PMM_PAGE_SIZE;
phy_page_count++;
}
}
}
}
uint32_t pmm_alloc_page()
{
assert(pmm_stack_top != 0, "out of memory");
uint32_t page = pmm_stack[pmm_stack_top--];
return page;
}
void pmm_free_page(uint32_t p)
{
assert(pmm_stack_top != PAGE_MAX_SIZE, "out of pmm_stack stack");
pmm_stack[++pmm_stack_top] = p;
}
|
解析:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| void init_pmm()
{
mmap_entry_t *mmap_start_addr = (mmap_entry_t *)glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_addr;
mmap_entry_t *mmap_end_addr = (mmap_entry_t *)glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_addr + glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_length;
mmap_entry_t *map_entry;
for (map_entry = mmap_start_addr; map_entry < mmap_end_addr; map_entry++) {
if (map_entry->type == 1 && map_entry->base_addr_low == 0x100000) {
uint32_t page_addr = map_entry->base_addr_low + (uint32_t)(kern_end - kern_start);
uint32_t length = map_entry->base_addr_low + map_entry->length_low;
while (page_addr < length && page_addr <= PMM_MAX_SIZE) {
pmm_free_page(page_addr);
page_addr += PMM_PAGE_SIZE;
phy_page_count++;
}
}
}
}
|
- 通过
glb_mboot_ptr 获取内存映射的起始和结束地址。
- 遍历每个内存映射条目,检查是否是可用内存并且起始地址是
0x100000(1MB以上)。
- 计算从内核结束位置开始的内存页地址,并按页存储到内存管理栈中。
- 使用
pmm_free_page() 函数将每个页地址放入栈中。
while循环中:
map_entry->base_addr_low:这是内存映射条目的基地址,表示内存块的起始地址。
map_entry->length_low:这是内存映射条目的长度,表示内存块的大小。
page_addr:当前正在处理的内存页的地址。
length:内存块的结束地址,用于确定内存块的范围。
PMM_MAX_SIZE:系统支持的最大物理内存大小,在此假设为512MB。
pmm_free_page(page_addr):将当前页地址放入内存管理栈中。
page_addr += PMM_PAGE_SIZE:将页地址移动到下一个页框(假设页框大小为4KB)。
phy_page_count++:增加已处理的页框计数。
init/entry.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| #include "types.h"
#include "console.h"
#include "debug.h"
#include "gdt.h"
#include "idt.h"
#include "timer.h"
#include "pmm.h"
int kern_entry(){
init_debug();
init_gdt();
init_idt();
console_clear();
printk_color(rc_black, rc_green, "Hello OS!!!\n");
init_timer(200);
printk("kernel in memory start: 0x%08X\n", kern_start);
printk("kernel in memory end: 0x%08X\n", kern_end);
printk("kernel in memory used: %d KB\n\n", (kern_end - kern_start + 1023) / 1024);
show_memory_map();
init_pmm();
printk_color(rc_black, rc_red, "\nThe Count of Physical Memory Page is: %u\n\n", phy_page_count);
uint32_t allc_addr = NULL;
printk_color(rc_black, rc_light_brown , "Test Physical Memory Alloc :\n");
allc_addr = pmm_alloc_page();
printk_color(rc_black, rc_light_brown , "Alloc Physical Addr: 0x%08X\n",allc_addr);
allc_addr = pmm_alloc_page();
printk_color(rc_black, rc_light_brown , "Alloc Physical Addr: 0x%08X\n",allc_addr);
allc_addr = pmm_alloc_page();
printk_color(rc_black, rc_light_brown , "Alloc Physical Addr: 0x%08X\n",allc_addr);
allc_addr = pmm_alloc_page();
printk_color(rc_black, rc_light_brown , "Alloc Physical Addr: 0x%08X\n",allc_addr);
return 0;
}
|
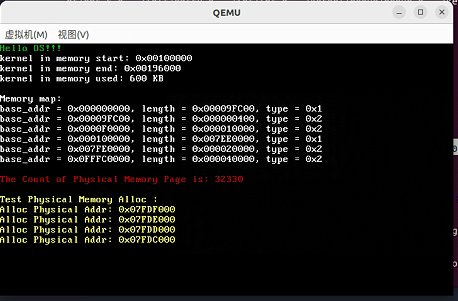
因为是用栈 进行管理的,所以最先分配的物理内存地址是高地址