11.内核堆管理的实现 目前已经实现了页管理,但是在需要分配小内存的时候,比较容易造成内部碎片 , — 实现内核的堆管理算法
内部碎片指的是:内存中各种对齐规则的限制,导致分配的内存 大于 进程所需要的内存,因此会造成内部碎片
需要实现的功能:
分配内存
在内存释放的时候对连续的内存进行合并
在空闲内存过多的时候,将物理页释放给物理内存管理模块
关于堆的实现,选择最简单的侵入式链表管理方法
Linux: C语言实现范型数据结构 - 嵌入(侵入)式链表浅谈 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
侵入式链表(Intrusive Linked List)是一种链表实现方式,其中链表节点的链接信息嵌入在节点数据结构本身中。
减少了内存的开销
include/heap.c
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #ifndef INCLUDE_HEAP_H_ #define INCLUDE_HEAR_H_ #include "types.h" #define HEAP_START 0xE0000000 typedef struct header { struct header *prev ; struct header *next ; uint32_t allocated : 1 ; uint32_t length : 31 ; }header_t ; void init_heap () ;void *kmalloc (uint32_t len) ;void kfree (void *p) ;void test_heap () ;#endif
1 2 uint32_t allocated : 1 ; uint32_t length : 31 ;
C语言的位域,能够节省内存,允许精确控制每个成员的位宽,但是移植性较差
mm/heap.c 具体实现 除了上述的外部接口函数,还需要实现一些内部函数
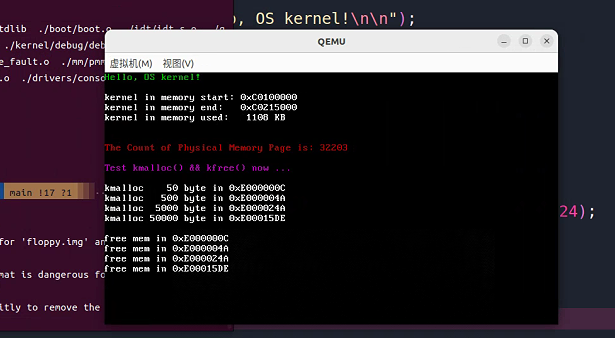
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 #include "debug.h" #include "pmm.h" #include "vmm.h" #include "heap.h" static void alloc_chunk (uint32_t start, uint32_t len) ;static void free_chunk (header_t *chunk) ;static void split_chunk (header_t *chunk, uint32_t len) ;static void glue_chunk (header_t *chunk) ;static uint32_t heap_max = HEAP_START;static header_t *heap_first;void init_heap () { heap_first = 0 ; } void *kmalloc (uint32_t len) { len += sizeof (header_t ); header_t *cur_header = heap_first; header_t *prev_header = 0 ; while (cur_header) { if (cur_header->allocated == 0 && cur_header->length >= len) { split_chunk(cur_header, len); cur_header->allocated = 1 ; return (void *)((uint32_t )cur_header + sizeof (header_t )); } prev_header = cur_header; cur_header = cur_header->next; } uint32_t chunk_start; if (prev_header) { chunk_start = (uint32_t )prev_header + prev_header->length; } else { chunk_start = HEAP_START; heap_first = (header_t *)chunk_start; } alloc_chunk(chunk_start, len); cur_header = (header_t *)chunk_start; cur_header->prev = prev_header; cur_header->next = 0 ; cur_header->allocated = 1 ; cur_header->length = len; if (prev_header) { prev_header->next = cur_header; } return (void *)(chunk_start + sizeof (header_t )); } void kfree (void *p) { header_t *header = (header_t *)((uint32_t )p - sizeof (header_t )); header->allocated = 0 ; glue_chunk(header); } void alloc_chunk (uint32_t start, uint32_t len) { while (start + len > heap_max) { uint32_t page = pmm_alloc_page(); map (pgd_kern, heap_max, page, PAGE_PRESENT | PAGE_WRITE); heap_max += PAGE_SIZE; } } void free_chunk (header_t *chunk) { if (chunk->prev == 0 ) { heap_first = 0 ; } else { chunk->prev->next = 0 ; } while ((heap_max - PAGE_SIZE) >= (uint32_t )chunk) { heap_max -= PAGE_SIZE; uint32_t page; get_mapping(pgd_kern, heap_max, &page); unmap(pgd_kern, heap_max); pmm_free_page(page); } } void split_chunk (header_t *chunk, uint32_t len) { if (chunk->length - len > sizeof (header_t )) { header_t *newchunk = (header_t *)((uint32_t )chunk + len); newchunk->prev = chunk; newchunk->next = chunk->next; newchunk->allocated = 0 ; newchunk->length = chunk->length - len; chunk->next = newchunk; chunk->length = len; } } void glue_chunk (header_t *chunk) { if (chunk->next && chunk->next->allocated == 0 ) { chunk->length = chunk->length + chunk->next->length; if (chunk->next->next) { chunk->next->next->prev = chunk; } chunk->next = chunk->next->next; } if (chunk->prev && chunk->prev->allocated == 0 ) { chunk->prev->length = chunk->prev->length + chunk->length; chunk->prev->next = chunk->next; if (chunk->next) { chunk->next->prev = chunk->prev; } chunk = chunk->prev; } if (chunk->next == 0 ) { free_chunk(chunk); } } void test_heap () { printk_color(rc_black, rc_magenta, "Test kmalloc() && kfree() now ...\n\n" ); void *addr1 = kmalloc(50 ); printk("kmalloc 50 byte in 0x%X\n" , addr1); void *addr2 = kmalloc(500 ); printk("kmalloc 500 byte in 0x%X\n" , addr2); void *addr3 = kmalloc(5000 ); printk("kmalloc 5000 byte in 0x%X\n" , addr3); void *addr4 = kmalloc(50000 ); printk("kmalloc 50000 byte in 0x%X\n\n" , addr4); printk("free mem in 0x%X\n" , addr1); kfree(addr1); printk("free mem in 0x%X\n" , addr2); kfree(addr2); printk("free mem in 0x%X\n" , addr3); kfree(addr3); printk("free mem in 0x%X\n\n" , addr4); kfree(addr4); }
init/entry.c 加入头文件以及初始化heap 和 添加测试test_heap() !!
!!!注意 vmm的初始化一定要在pmm之后
1 2 3 4 5 6 ... #include "heap.c" .... init_heap(); test_heap();
运行结果如下: